LeetCode 40. 组合总和 II 中等
题目描述
给定一个数组 candidates 和一个目标数 target ,找出 candidates 中所有可以使数字和为target的组合。
candidates 中的每个数字在每个组合中只能使用一次。
说明:
所有数字(包括目标数)都是正整数。解集不能包含重复的组合。示例 1:
javascript
输入: candidates = [10,1,2,7,6,1,5], target = 8,
所求解集为:
[
[1, 7],
[1, 2, 5],
[2, 6],
[1, 1, 6]
]示例 2:
javascript
输入: candidates = [2,5,2,1,2], target = 5,
所求解集为:
[
[1,2,2],
[5]
]来源:力扣(LeetCode)链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/combination-sum-ii 著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
解题思路
这道题也是一道组合题,但是这道题数组里面是存在重复元素的,组合题的话,为了更好地去重,我们可以先对数组进行排序,然后对于每一层如果相邻元素相同,就剪掉该分支即可。
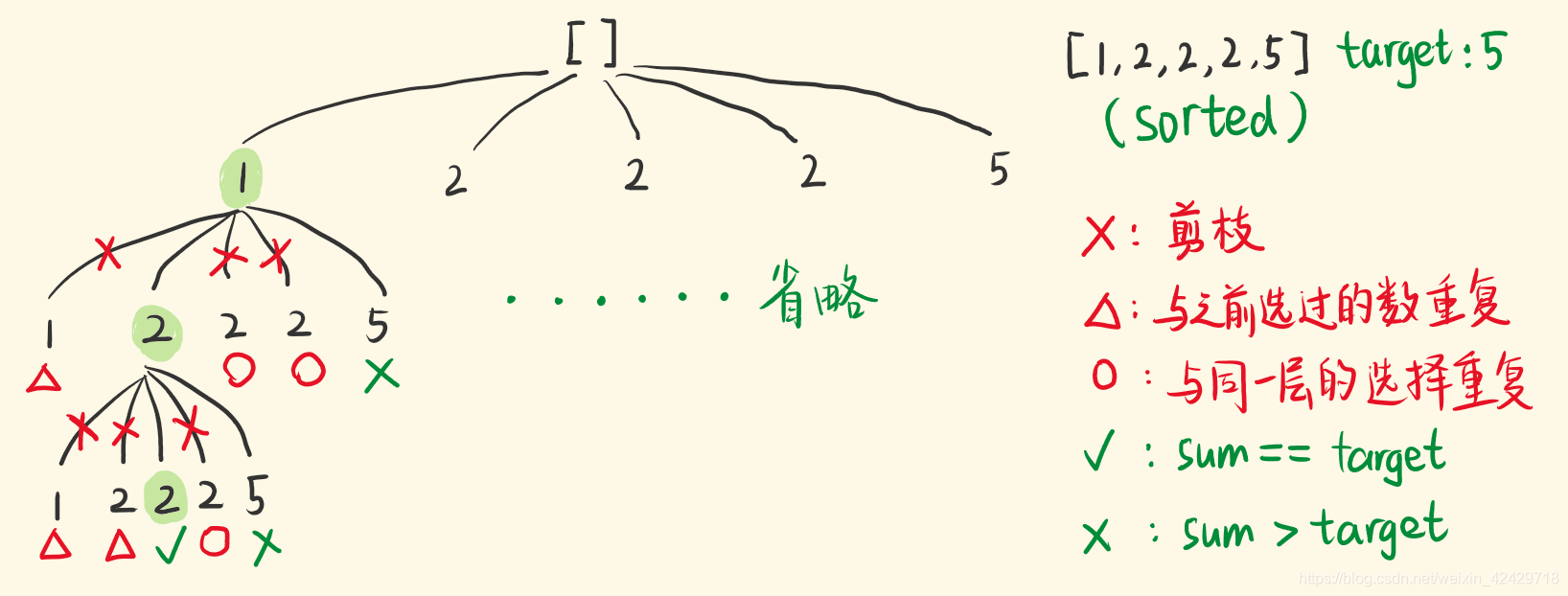
注意求和那里,如果只判断是否相等的话,可能会出现爆掉情况。
javascript
var combinationSum2 = function (candidates, target) {
let res = [];
candidates.sort((a, b) => a - b);
let dfs = (t, start, sum) => {
if (sum >= target) {
// 加这外层,超出范围了也终止,防爆栈
if (sum === target) {
res.push(t);
}
return;
}
// 组合
for (let i = start; i < candidates.length; i++) {
// 组合元素不能重复,去掉同一层重复的元素
if (i > start && candidates[i] == candidates[i - 1]) continue;
t.push(candidates[i]);
// 组合元素去重,即当前选择和下一层的不能重复
dfs(t.slice(), i + 1, sum + candidates[i]);
t.pop();
}
};
dfs([], 0, 0);
return res;
};cpp
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> combinationSum2(vector<int>& candidates, int target) {
vector<vector<int>> res;
vector<int> t;
sort(candidates.begin(), candidates.end());
dfs(candidates, target, 0, 0, t, res);
return res;
}
void dfs(vector<int>& candidates, int target, int start, int sum, vector<int>& t, vector<vector<int>>& res) {
if (sum >= target) {
if (sum == target) {
res.push_back(t);
}
return;
}
for (int i = start; i < candidates.size(); i++) {
if (i > start && candidates[i] == candidates[i - 1]) continue;
t.push_back(candidates[i]);
dfs(candidates, target, i + 1, sum + candidates[i], t, res);
t.pop_back();
}
}
};java
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum2(int[] candidates, int target) {
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> t = new ArrayList<>();
Arrays.sort(candidates);
dfs(candidates, target, 0, 0, t, res);
return res;
}
public void dfs(int[] candidates, int target, int start, int sum, List<Integer> t, List<List<Integer>> res) {
if (sum >= target) {
if (sum == target) {
res.add(new ArrayList<>(t));
}
return;
}
for (int i = start; i < candidates.length; i++) {
if (i > start && candidates[i] == candidates[i - 1]) continue;
t.add(candidates[i]);
dfs(candidates, target, i + 1, sum + candidates[i], t, res);
t.remove(t.size() - 1);
}
}
}python
class Solution:
def combinationSum2(self, candidates: List[int], target: int) -> List[List[int]]:
res = []
t = []
candidates.sort()
self.dfs(candidates, target, 0, 0, t, res)
return res
def dfs(self, candidates, target, start, sum, t, res):
if sum >= target:
if sum == target:
res.append(t[:])
return
for i in range(start, len(candidates)):
if i > start and candidates[i] == candidates[i - 1]: continue
t.append(candidates[i])
self.dfs(candidates, target, i + 1, sum + candidates[i], t, res)
t.pop()javascript
学如逆水行舟,不进则退 Kano
Kano